The Silent Workhorse: Understanding the Basics of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic systems are the unsung heroes of countless industries, from manufacturing to robotics. While air compressors and filters play vital roles, the pneumatic cylinder is often the component that brings the power of compressed air to life, translating it into tangible motion. It’s the “muscle” of a pneumatic system, enabling automation and efficiency in ways you might not even realize.
What Exactly Is a Pneumatic Cylinder?
At its core, a pneumatic cylinder is a mechanical device that uses the force of compressed air to produce a linear motion. Think of it like a syringe, but instead of pushing fluid, it’s pushing a rod using air pressure.
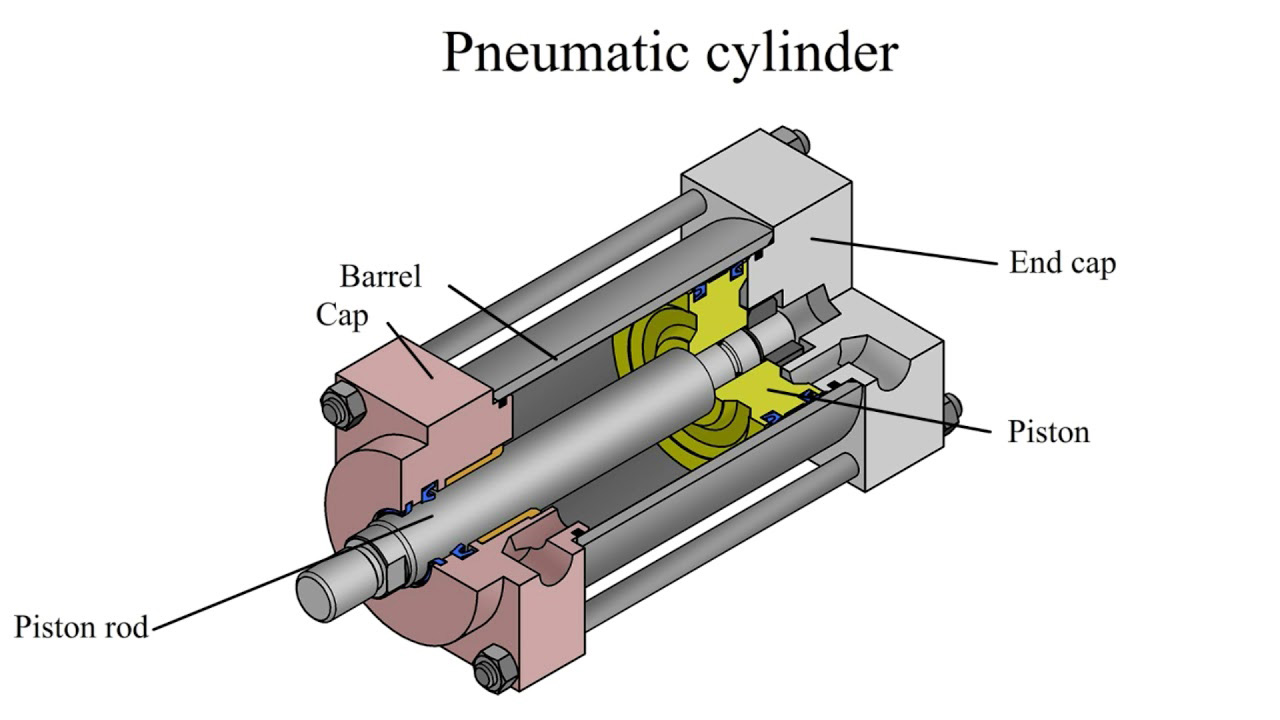
Here’s a breakdown of its main components:
- Barrel (or Cylinder Body): The main housing, typically a hollow tube, where the magic happens.
- Piston: A disc-shaped component that fits snugly inside the barrel.
- Piston Rod: Attached to the piston, this rod extends and retracts out of the cylinder, providing the linear motion.
- End Caps: These seal the ends of the barrel and contain the air ports where compressed air enters and exits.
- Seals: Crucial for preventing air leaks, ensuring that the compressed air effectively pushes the piston.
How Do They Work? The Simple Science
The operation is surprisingly straightforward:
- Air In, Rod Out: When compressed air is introduced into one end of the cylinder (say, the back end), the pressure builds up and pushes against the piston.
- Linear Motion: This force causes the piston to move along the length of the barrel, extending the piston rod.
- Air Out, Rod In: To retract the rod, air is either vented from the first port and introduced into the other end (for double-acting cylinders), or a spring mechanism pulls the rod back (for single-acting cylinders).
Types of Pneumatic Cylinders: Tailoring Motion to Your Needs
Not all cylinders are created equal. They come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
- Single-Acting Cylinders: These have one port for air input. Air pushes the rod out, and a spring or external force returns it to its original position. They’re simpler and more cost-effective for applications requiring motion in only one direction.
- Double-Acting Cylinders: The most common type, these have two ports. Compressed air can be applied to either side of the piston, allowing for controlled motion in both extension and retraction. This offers greater control and power.
- Rodless Cylinders: Unlike traditional cylinders with external rods, these move a carriage along the cylinder body, ideal for applications where space is limited or long strokes are required.
Where Do You Find Them? The Ubiquitous Presence
Pneumatic cylinders are the hidden power behind a vast array of everyday processes and industrial operations:
- Manufacturing: Used for clamping, pushing, lifting, and sorting products on assembly lines.
- Packaging: Essential for opening and closing flaps, sealing, and moving packages.
- Robotics: Providing precise movements for robotic arms and grippers.
- Automotive: Found in paint booths, welding equipment, and even in some car assembly processes.
- Food and Beverage: Utilized in filling machines, capping, and conveyor systems.
- Medical Devices: Enabling precise movements in hospital beds and other equipment.
Why Pneumatic Cylinders? The Advantages
Their widespread use isn’t by chance. Pneumatic cylinders offer several compelling benefits:
- Cleanliness: Unlike hydraulic systems that use oil, pneumatic systems use air, making them ideal for cleanroom environments and industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
- Cost-Effective: Often more affordable to install and maintain than hydraulic or electric alternatives for many applications.
- Speed: Can achieve very high operating speeds, crucial for high-volume production.
- Safety: Compressed air is non-flammable and systems are generally less prone to overheating, making them safer in many environments.
- Simplicity: Relatively simple in design and operation, leading to easier troubleshooting and maintenance.
Pneumatic cylinders might be silent, but their impact is anything but. They are the unseen heroes, efficiently and reliably providing the linear motion that keeps our modern world moving. We understand the critical role these components play in your operations, and we’re here to help you find the right pneumatic solutions for your specific needs. Contact our Product Specialists today to learn more at sales@processpneumatics.com.



